MOSFET High-Side Switch Design Tips for Electronics Enthusiasts
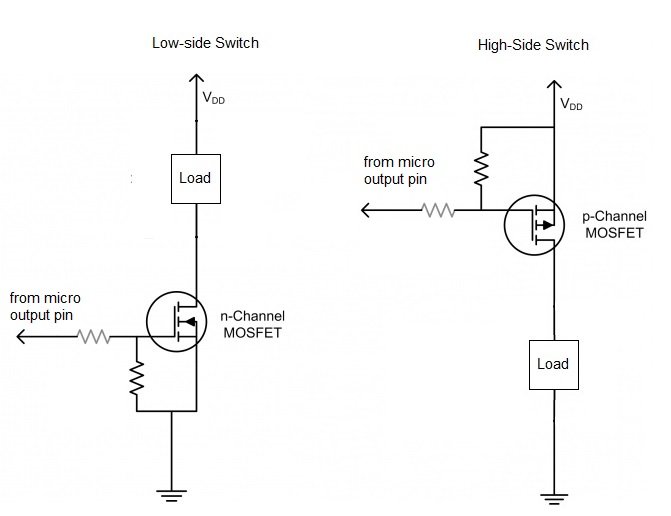
When designing circuits, particularly when controlling high-power loads, understanding how to work with MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) is crucial. One common challenge that hobbyists and engineers face is using MOSFETs in high-side switching applications. This means controlling a load connected to the positive side of the power supply (as opposed to the negative side).
The Problem :
In a high-side switch, the gate voltage of the MOSFET needs to be higher than the source voltage to turn it on. This can be tricky because the source is connected to the load and the power supply, which means that the gate voltage must be pushed even higher than usual to ensure the MOSFET fully turns on.
The Solution :
To solve this, use a gate driver or bootstrap circuit. These components can “boost” the gate voltage above the source, ensuring the MOSFET switches on properly. A simple way to implement this is by using a transformer or a dedicated high-side MOSFET driver IC.
Practical Example :
Imagine you’re designing a circuit to control a motor. The motor is powered from a 12V supply, and you want to use a MOSFET as a high-side switch. Without a gate driver, you won’t be able to turn the MOSFET on fully, leading to inefficiency or even failure. By adding a gate driver IC, you can ensure the MOSFET gets enough voltage at its gate to turn on completely.
Sample Calculation :
To calculate the required gate resistor for proper switching, let’s say you want a gate charge of 10nC for the MOSFET and a driver current of 1mA. The gate resistor value would be:
R=IV=1mA10V=10kΩ
This ensures a smooth transition in switching without excessive power loss.
Shop Now :
For high-quality MOSFET and gate driver ICs, visit our [Make in India shop] and start building your next project! Support India’s innovation by purchasing from SmartXProKits.in today!




















