Reverse Voltage Protection for 5V Circuits
🔧 The Problem: Accidental Reverse Voltage in 5V Systems
Reverse voltage—when the power supply is connected backward—is a common mistake in prototyping. In 5V systems, this can instantly damage sensitive ICs, sensors, or even your microcontroller. The issue often arises during breadboarding or quick wire swaps, especially by beginners.
🛠️ The Solution: Simple Reverse Voltage Protection
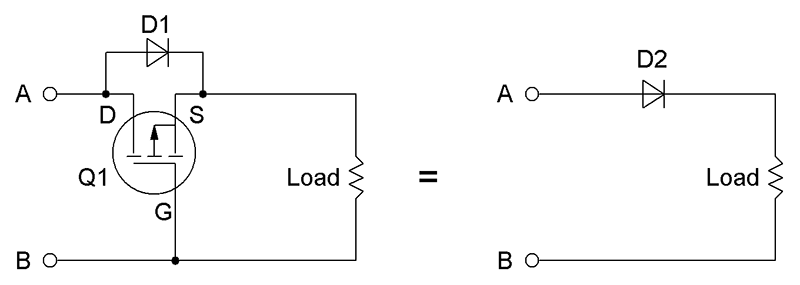
To prevent this, add a reverse voltage protection circuit using a Schottky diode or a P-channel MOSFET on the power input. While a diode drops some voltage (~0.3–0.7V), a P-MOSFET in the correct orientation can provide near-zero voltage drop and efficient protection.
🏠 Practical Example: Arduino + Sensor Project
Suppose you’re powering an Arduino Nano and a DHT22 sensor with a 5V battery pack. If you accidentally reverse the battery leads, the microcontroller and sensor could fry. Add a P-channel MOSFET (like IRF9540) between the battery and the VCC line with proper gate biasing—it will block current if the polarity is incorrect.
📐 Sample Calculation: Gate Resistor
For a P-MOSFET, use a gate resistor (~10kΩ) to pull the gate high.
When VIN is 5V, the source is also at 5V.
The gate must be pulled to GND to turn the MOSFET on (Vgs = -5V), allowing current flow only in correct polarity.
🛍️ Product Suggestion
👉 Shop now at SmartXProKits.in
🇮🇳 Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















