Protecting MOSFET Gate-to-Source: Easy Guide for Prototypers
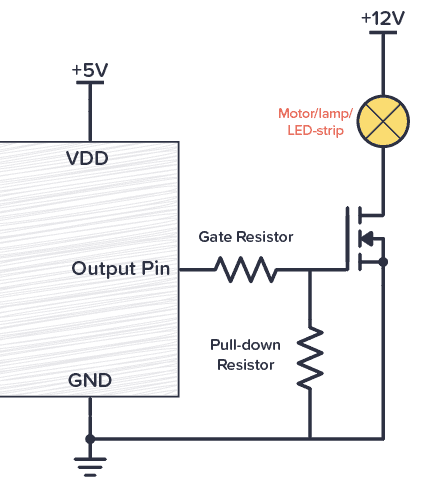
The Problem :
MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) are widely used for switching in power electronics. However, the gate-to-source (G-S) junction is highly sensitive to voltage spikes. If the gate voltage exceeds the MOSFET’s maximum threshold (typically 20V for most MOSFETs), it can damage the internal gate oxide, leading to permanent failure.
The Solution :
A simple and effective way to protect the MOSFET is by adding a Zener diode across the gate-to-source terminals. The Zener diode clamps the voltage, ensuring the gate voltage never exceeds the safe limit.
Practical Example :
Consider a DC motor control project using an IRF540N MOSFET driven by a 12V microcontroller. Without protection, a voltage spike can damage the MOSFET. Adding a 12V Zener diode (e.g., 1N4742A) across the gate-to-source prevents the voltage from exceeding 12V, safeguarding the MOSFET.
Sample Calculation :
To limit current through the Zener diode, place a 100Ω resistor in series with the gate. The power dissipated by the resistor can be calculated using:
P=RV2=100122=1.44W
A 1W or higher resistor is sufficient to handle this power safely.
Product Suggestions :
Get quality Made in India components to enhance your circuits:
IRF540N MOSFET – Ideal for switching applications.
1N4742A Zener Diode – Protects the gate from overvoltage.
Safeguard your MOSFETs with simple and affordable protection! Shop now at SmartXProKits.in and support India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















