MOSFET Gate Drive Isolation Tips – Keep Your Switches Safe
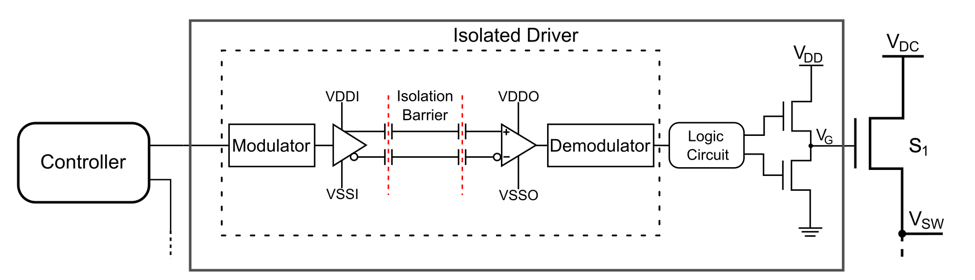
When switching high-power loads using MOSFETs, gate drive isolation becomes essential. Without it, you risk unwanted oscillations, false switching, or even gate damage—especially in half-bridge or high-side switching configurations.
👨🔧 The Problem :
The gate of a MOSFET is like a capacitor—it needs controlled charging and discharging. If your microcontroller shares the same ground as your power MOSFET’s source (especially in high-side setups), noise can couple back, causing unpredictable behavior.
Solution: Use an isolated gate driver or an opto-isolator to keep your control and power sections electrically separate.
🛠️ The Solution :
An engineer in Bengaluru designing a BLDC motor driver found the motor jittered at high RPM. After adding an IR2110 gate driver with proper bootstrap and isolation, the circuit stabilized and performed flawlessly.
🧮 Sample Calculation : Gate Resistor
For a gate charge Qg=20nC and desired switching time t=100nst = 100nst=100ns:
I=Qg/t=20nC/100ns=0.2A
Using V=IR, and V=10VV = 10VV=10V,
R=V/I=10/0.2=50Ω gate resistor works well.
🔧 Recommended Components :
Shop now at SmartXProKits.in
🇮🇳 Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















