Low Voltage Smart Plug Power Design – A Beginner-Friendly Guide
Designing smart plugs is exciting—but safely powering them can be a challenge. Let’s break it down for hobbyists, engineers, and prototypers in India who want a clean, compact solution using Made in India components.
⚠️ The Problem: Powering Smart Plugs Safely
Smart plugs typically use microcontrollers like the ESP8266 or ESP32, which run on 3.3V or 5V DC. But India’s mains voltage is 230V AC. Connecting directly is dangerous and can damage components or cause electrical hazards.
🔧 The Solution: Step-Down Power Supply Design
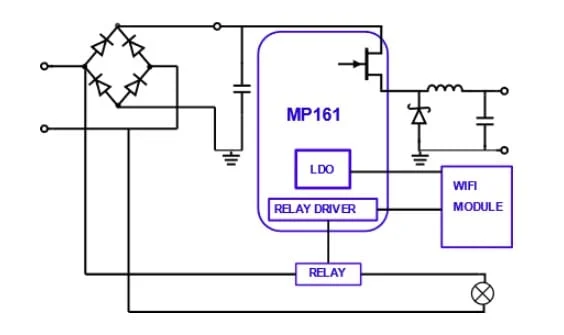
To convert 230V AC to low voltage DC, use a step-down power circuit with:
A capacitive power supply or isolated transformer for AC to DC conversion.
A voltage regulator (like AMS1117 or 7805) to stabilize voltage.
Proper safety elements: fuses, TVS diodes, and optocouplers for isolation.
💡 Practical Example: DIY Wi-Fi Smart Plug
Let’s say you’re building a smart plug with an ESP8266 that switches a lamp ON/OFF over Wi-Fi. If you skip the step-down and connect the chip directly to AC, it will fry instantly. Instead, use a mini buck converter (230V AC to 5V DC), followed by a regulator to 3.3V.
Add a MOSFET to switch the load, controlled by the ESP chip.
🧮 Sample Calculation: Power Requirements
Your ESP8266 consumes around 200mA at 3.3V.
Power = Voltage × Current
= 3.3V × 0.2A = 0.66W
Add 30% for regulator and Wi-Fi spikes →
Required: ~0.86W → Use a 1W+ rated module.
Choose a buck converter and MOSFET rated for your load (e.g., 1A or higher).
🛠️ Product Suggestion (Made in India)
Build your design with locally sourced, reliable parts:
⚡ MOSFET Modules – For switching AC loads safely
🧪 Flux Paste – For solid solder joints and long-lasting circuits
🛍️ Shop now at SmartXProKits.in
Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















