Choosing the Right MOSFET Gate Driver: A Quick Guide
🛠️ The Problem :
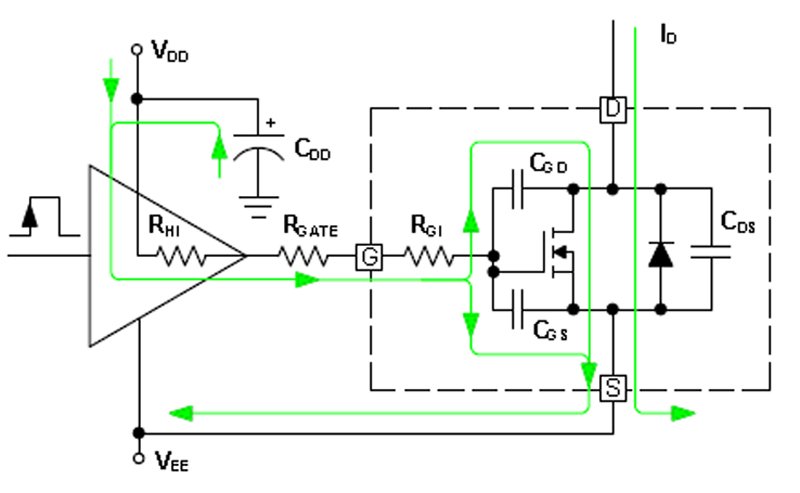
When driving a power MOSFET in your circuit, especially in high-speed switching applications like motor drivers, inverters, or SMPS, directly controlling the gate from a microcontroller can result in slow switching, overheating, and inefficiency. This is because MOSFET gates require significant current to charge/discharge rapidly.
✅ The Solution :
The fix is to use a MOSFET gate driver—a buffer circuit designed to quickly supply the current needed to switch the MOSFET on and off. A good gate driver reduces switching losses, improves performance, and protects your microcontroller.
🔍 Practical Example :
Let’s say you’re using an IRFZ44N MOSFET to control a 12V motor with a PWM signal from an Arduino. The Arduino can’t supply the 1–2A current needed for fast switching. Adding a gate driver like the IR2110 or TC4420 makes switching fast and clean, avoiding MOSFET heating.
📏 Sample Calculation :
Gate charge (Qg) of IRFZ44N ≈ 67nC
Desired switching time (t) = 100ns
Required current:
I = Qg / t = 67nC / 100ns = 0.67A
This is beyond most microcontrollers—hence, use a gate driver.
🛒 Product Suggestions (Made in India)
Shop now at SmartXProKits.in — Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















