Reverse Current Protection in LED Drivers – A Simple Guide for Hobbyists & Engineers
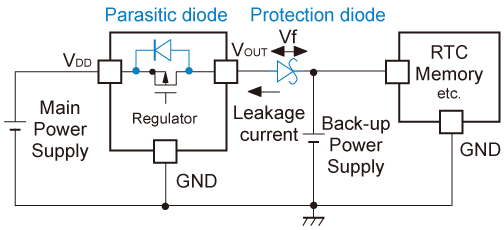
When designing circuits, especially for LED drivers, one common issue you might encounter is reverse current. This happens when current flows in the wrong direction, potentially damaging components like LEDs or drivers. In this post, we’ll explain how reverse current protection works and show you how to fix this issue in simple terms.
The Problem :
Reverse current occurs when the polarity of your circuit is reversed, causing current to flow in the opposite direction. In LED drivers, this can burn out the LEDs or even damage the power supply. To fix this, you can use a diode to prevent current from flowing backward. The diode allows current to flow only in the correct direction, protecting your components.
Practical Example :
Imagine you’re designing a simple LED circuit to power a strip of LEDs. If you connect the power supply in reverse, the LEDs won’t light up and might get damaged. To prevent this, add a diode in series with the LED driver. The diode only allows current to flow when the power supply is connected correctly, preventing reverse current from reaching the LEDs.
Sample Calculation :
Let’s say you are using a 12V LED driver.
The diode should have a voltage drop of about 0.7V (for a typical silicon diode).
So, with a 12V input:
- Voltage available for the LED driver = 12V – 0.7V = 11.3V.
Shop Now :
To implement reverse current protection effectively, check out high-quality diodes and MOSFETs for your projects—Made in India for superior performance.
Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















