Reverse Current Protection in Automotive – A Must-Have!
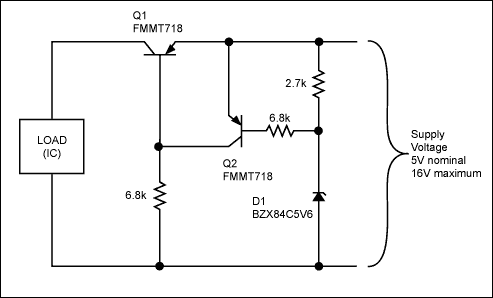
⚠️ The Problem :
In automotive electronics, reverse current can damage sensitive circuits when power flows the wrong way—especially during battery swaps or wiring mistakes. This is common in 12V or 24V systems where relays, LEDs, or ECUs are connected directly to the battery.
🛠️ The Solution :
To prevent reverse current, use MOSFET-based reverse polarity protection. Unlike diodes, which drop voltage (0.7V or more), MOSFETs offer near-zero loss when configured properly (P-channel for high-side or N-channel for low-side with gate control).
🔧 Practical Example :
Imagine you’re powering a dashcam directly from your car’s 12V line. Without protection, if someone accidentally connects the wires in reverse, the dashcam gets fried. By placing a P-Channel MOSFET with the source to battery and gate pulled to ground via a resistor, it blocks reverse current elegantly.
📐 Sample Calculation :
If your dashcam draws 1A and you use a Schottky diode with 0.5V drop, power loss =
P = V × I = 0.5V × 1A = 0.5W (wasted as heat).
With a low-R<sub>DS(on)</sub> MOSFET (say 30mΩ):
P = I² × R = 1² × 0.03 = 0.03W – much more efficient!
🛒 Product Tie-In :
Get automotive-grade MOSFETs and flux for your soldering needs here:
Shop now at SmartXProKits.in
🇮🇳 Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















