Low Voltage Smart Light Power Guide – DIY Tips
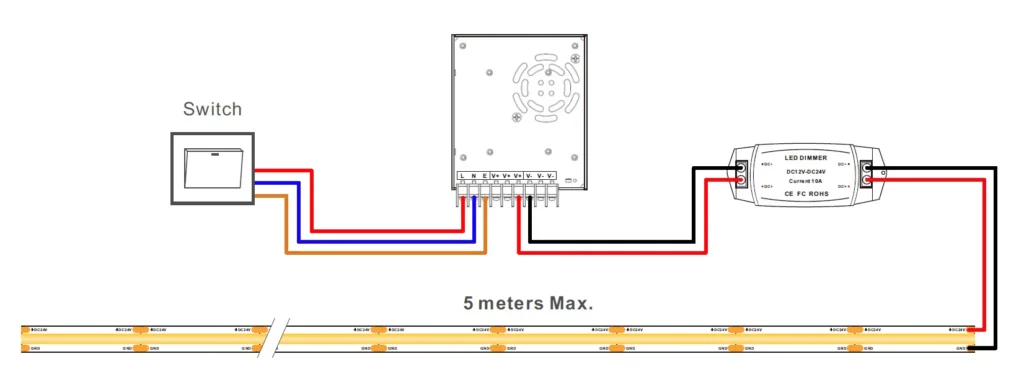
💡 The Problem: Powering Smart Lights on Low Voltage
Smart lighting systems often run on low voltage (5V–12V) to ensure safety and compatibility with microcontrollers. However, unstable power sources can cause flickering, reduced LED lifespan, or Wi-Fi/Bluetooth disconnections in IoT setups. The root cause? Poor regulation and incorrect current handling.
🛠️ The Solution: Clean, Stable Power Supply Design
To keep your smart lights running smoothly:
Use a low-dropout (LDO) regulator or buck converter to step down from 12V to 5V efficiently
Add decoupling capacitors (10μF + 0.1μF) close to your LED controller
Ensure MOSFETs used for switching are logic-level and have low R<sub>DS(on)</sub>
🧠 Practical Example: Home Automation with ESP8266
An engineer in Bengaluru created a smart bedroom light using an ESP8266 and WS2812 LEDs. Initially, the lights glitched during Wi-Fi use. Switching from a basic 7805 to a buck converter fixed the issue, providing 5V at 1.5A with less heat and better stability.
🔢 Sample Calculation: Power Requirement
Let’s say your LED strip draws 1A at 5V:
Power = Voltage × Current = 5V × 1A = 5W
Add 20% margin → choose a power supply rated for 6W or more.
🛒 Product Suggestion: Made in India Picks
Use reliable MOSFETs and buck converters from Indian manufacturers:
👉 Shop now at SmartXProKits.in — Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















