Low Voltage Arduino Power Reference – Solving Power Issues for Your Projects
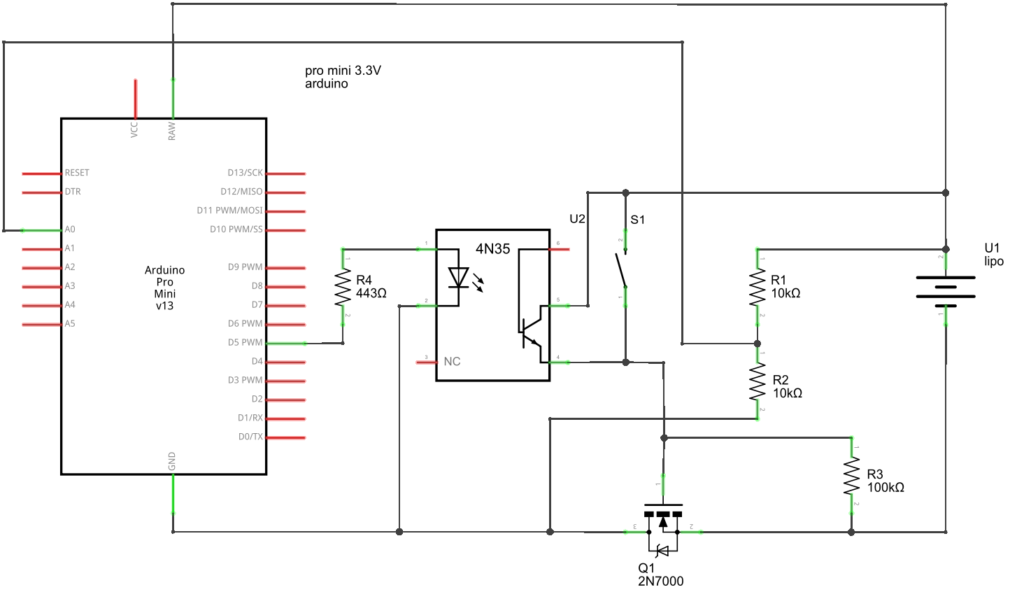
When working with Arduino projects, one common issue that electronics hobbyists and engineers face is low voltage power supply. This can lead to unstable behavior, unreliable sensors, or even malfunctioning circuits. But don’t worry—this problem has a straightforward fix!
The Problem :
If you’re powering your Arduino from a USB port or low-capacity adapter, the voltage may drop below the required 5V or 3.3V, causing instability. In many cases, sensors and modules require a steady 5V supply to function properly. When the power drops, your system may reset or behave erratically.
The Solution :
To ensure your Arduino gets a stable power supply, you can use a voltage regulator or a higher capacity power adapter. This ensures your board receives consistent power, avoiding voltage dips.
Practical Example :
Imagine you’re working on a weather station with an Arduino, a temperature sensor, and an LCD display. You notice that when the Arduino is connected to a weak USB power source, the LCD flickers, and readings become unreliable. By switching to a 5V regulated adapter or a power bank with sufficient output, your system will stabilize, and your project will run smoothly.
Sample Calculation :
Let’s say your Arduino draws 200mA at full load, and you’re using a 5V adapter.
The power usage can be calculated as:
- Power (P) = Voltage (V) × Current (I)
- P = 5V × 0.2A = 1W.
Products Suggestion :
For better power management in your projects, check out our range of voltage regulators and 5V adapters, all Made in India. Explore products like:
Shop now at SmartXProKits.in for reliable and affordable components. Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















