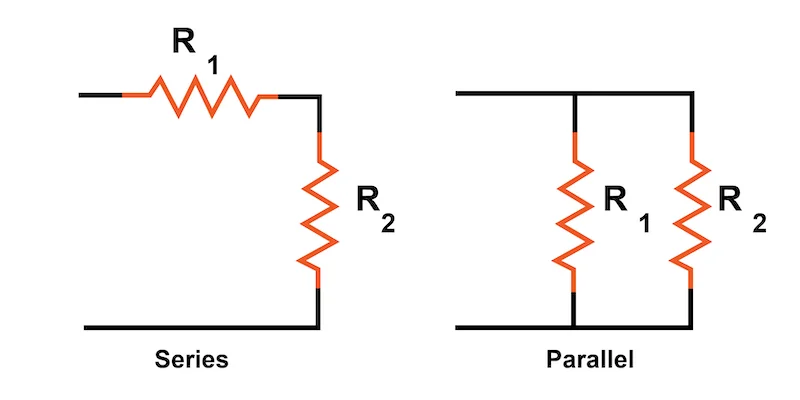
Let’s explore the differences between series and parallel circuits, and understand each concept more comprehensively:
Series Circuit:
Definition:
- A series circuit is a circuit arrangement where components are connected end-to-end, forming a single pathway for the current.
Current Flow:
- The same current flows through all components in a series circuit.
Voltage Distribution:
- The total voltage of the circuit is the sum of the individual voltages across each component.
Resistance:
- The total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of the individual resistances.
Brightness (for bulbs or LEDs):
- Bulbs or LEDs in a series circuit share the same current, so if one goes out, they all go out.
Advantages:
- Simple construction.
- Easy to analyze and calculate.
Disadvantages:
- If one component fails, the entire circuit is affected.
Parallel Circuit:
Definition:
- A parallel circuit is a circuit arrangement where components are connected in multiple pathways, providing separate paths for the current.
Current Flow:
- Current is divided among the branches, and each component has its own current.
Voltage Distribution:
- All components in a parallel circuit have the same voltage across them.
Resistance:
- The reciprocal of the total resistance in a parallel circuit is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
Brightness (for bulbs or LEDs):
- Bulbs or LEDs in parallel circuits have the same voltage, so if one goes out, the others remain lit.
Advantages:
- If one component fails, the others remain unaffected.
- Independent operation of components.
Disadvantages:
- More complex than series circuits.
Conclusion:
Series Circuit: Components are connected end-to-end, and the same current flows through all of them.
Parallel Circuit: Components are connected in multiple paths, and the current is divided among them.
Understanding series and parallel circuits is crucial for designing and analyzing electronic circuits, and it forms the foundation for more complex circuit configurations.
Tag : difference between rlc series and parallel circuit difference between series and parallel connection in battery difference between series and parallel connection in resistance difference between series and parallel connection of solar panels difference between series and parallel magnetic circuit
Written by kanchan kan
- Industrial Automation141141 products
- Cooling Fan44 products
- Indicators1111 products
- Plastic Casing66 products
- Sensor2323 products
- Sleeve and cables55 products
- SMPS88 products
- Solid State Relay Module22 products
- Switches1818 products
- Temprature Sensor11 product
- 3D Printing180180 products
- 3D printing110110 products
- Combination Kit4747 products
- Electronic743743 products
- Audio55 products
- Battery/Charger Accessories2828 products
- Capacitors6464 products
- Connector4646 products
- cooling fan11 product
- Diode3535 products
- Displays1212 products
- IC and Chips6565 products
- IOT and Wireless99 products
- Leds2424 products
- Microcontrollers55 products
- Modules/Shield7575 products
- MOSFET / IGBT1414 products
- Power Supply2525 products
- Resistors130130 products
- Sensors5959 products
- SMD2828 products
- Switches1414 products
- Transistors6868 products
- Wire and Cables1212 products
- Hardware3232 products
- Hand Tools1414 products
- Hardware Accessories1414 products
- Printing22 products
- RC Plane and Drone99 products
- Robotic147147 products
- BO Motors1313 products
- General Purpose DC Motors2929 products
- Motor Drivers88 products
- Robotic Wheels & Tyres1414 products
- Servo Motor2727 products
- Stepper Motors88 products
- Synchronous Motor11 product
- Science Fair Project7070 products
- Final Year Ready Project Kit11 product
- STEM KIT2222 products
- E Books88 products

