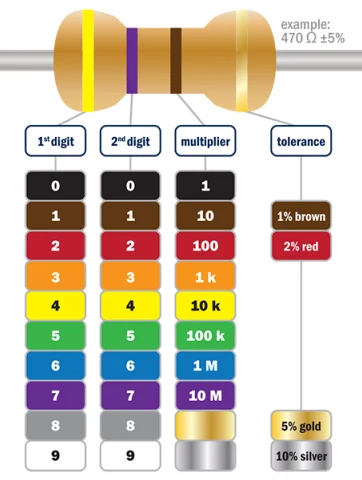
The Guide to Resistor Values is an essential reference for anyone working with electronic circuits. Resistors are fundamental components that limit the flow of electric current, and their values are crucial for designing and building circuits. Here’s what you need to know about the guide to resistor values:
- Resistor Color Code:
- The most common way to represent resistor values is through a color code. Different colors correspond to different digits and multipliers, allowing you to determine the resistor value by examining its color bands.
- The color code typically consists of three to six colored bands, indicating resistance, tolerance, and sometimes temperature coefficient.
- Standard Resistor Values:
- Resistors are manufactured in standard values according to the E-series (preferred number series). The most common series include E6, E12, E24, E48, E96, and E192.
- For example, in the E12 series, the values are spaced such that each value is approximately 20% higher than the previous one.
- EIA-96 (E96) Series:
- The E96 series is commonly used in precision applications. It provides a wider range of values with tighter tolerances compared to the E12 or E24 series.
- It includes 96 values per decade, offering a finer selection of resistance
- Preferred Resistor Values:
- Certain values are considered “preferred” because they are readily available and commonly used. These values are part of the standard E-series.
- Examples of preferred resistor values include 10, 47, 100, 220, 470, 1k, 4.7k, 10k, 47k, 100k, etc.
- Tolerance:
- The tolerance of a resistor indicates the permissible deviation from the specified resistance Common tolerances include 1%, 2%, 5%, and 10%.
- Precision applications often require resistors with lower tolerances to ensure accuracy.
- Power Rating:
- The power rating of a resistor indicates how much power it can dissipate without overheating. Common power ratings include 0.125W, 0.25W, 0.5W, 1W, and higher.
- Select a resistor with a power rating greater than or equal to the calculated power dissipation in a circuit.
- Surface Mount Resistors (SMD):
- Surface mount resistors, or SMD resistors, are compact resistors designed for surface mount technology (SMT) applications.
- They are labeled with a three- or four-digit code, and the EIA-96 series is commonly used for SMD
- Resistor Networks:
- Resistor networks consist of multiple resistors packaged together in a single component. They are commonly used in integrated circuits and applications where space is limited.
- Applications:
- Resistors are used in various electronic circuits for current limiting, voltage dividing, biasing transistors, setting the gain of amplifiers, and many other functions.
Understanding the guide to resistor values is crucial for selecting the right resistors for your circuit design. Whether you are deciphering color codes, choosing standard values, or considering tolerances, a solid understanding of resistor values is essential for successful electronic projects.
Written by kanchan kan
- Industrial Automation141141 products
- Cooling Fan44 products
- Indicators1111 products
- Plastic Casing66 products
- Sensor2323 products
- Sleeve and cables55 products
- SMPS88 products
- Solid State Relay Module22 products
- Switches1818 products
- Temprature Sensor11 product
- 3D Printing189189 products
- 3D printing118118 products
- Combination Kit4747 products
- Electronic743743 products
- Audio55 products
- Battery/Charger Accessories2828 products
- Capacitors6464 products
- Connector4646 products
- cooling fan11 product
- Diode3535 products
- Displays1212 products
- IC and Chips6565 products
- IOT and Wireless99 products
- Leds2424 products
- Microcontrollers55 products
- Modules/Shield7575 products
- MOSFET / IGBT1414 products
- Power Supply2525 products
- Resistors130130 products
- Sensors5959 products
- SMD2828 products
- Switches1414 products
- Transistors6868 products
- Wire and Cables1212 products
- Hardware3232 products
- Hand Tools1414 products
- Hardware Accessories1414 products
- Printing22 products
- RC Plane and Drone99 products
- Robotic147147 products
- BO Motors1313 products
- General Purpose DC Motors2929 products
- Motor Drivers88 products
- Robotic Wheels & Tyres1414 products
- Servo Motor2727 products
- Stepper Motors88 products
- Synchronous Motor11 product
- Science Fair Project7070 products
- Final Year Ready Project Kit11 product
- STEM KIT2222 products
- E Books88 products




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.