SMPS High-Power Layout Guide – Design Like a Pro
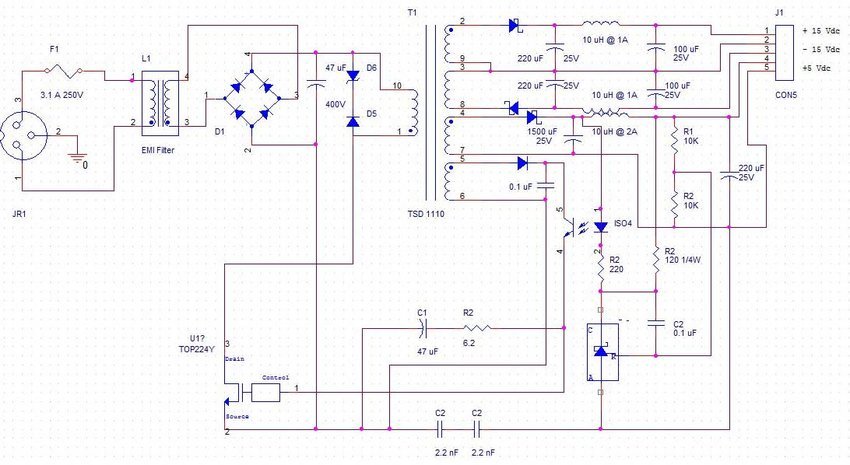
Designing a high-power SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) requires more than just the right components—it needs the right PCB layout. Whether you’re building a DIY inverter or a lab bench supply, layout mistakes can cost you efficiency and reliability.
🔧 The Problem :
High currents and fast switching in SMPS circuits cause electromagnetic interference (EMI), voltage spikes, and heating. Long traces, narrow tracks, or messy grounding lead to oscillations, component stress, and even burnt PCBs.
✅ The Solution :
To fix these issues:
Minimize loop areas in switching paths by placing the MOSFET, diode, and inductor close together.
Use wide traces or copper pours for high-current paths.
Maintain a solid ground plane to reduce noise and improve stability.
Place ceramic capacitors (like 100nF) close to IC power pins for effective decoupling.
🔍 Practical Example :
If you’re designing a 12V, 5A LED driver SMPS:
The output current is 5A.
According to IPC-2221, for 1 oz copper and 10°C temp rise, you need a trace width of ~3mm.
Use 5mm trace width for safety and future scaling.
📏 Sample Calculation :
Let’s say:
Output Current = 5A
Trace length = 2cm
Required trace width ≈ 3mm (for 1oz copper, 10°C rise)
Use a wider 5mm trace or a copper fill for efficiency and low resistance.
🛒 Product Suggestion: Made in India Tools That Matter
For efficient SMPS builds, use Made in India MOSFETs and flux to ensure low-resistance switching and clean solder joints:
Shop now at SmartXProKits.in — Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!



















