MOSFET Switching Speed Limits – Why It Matters
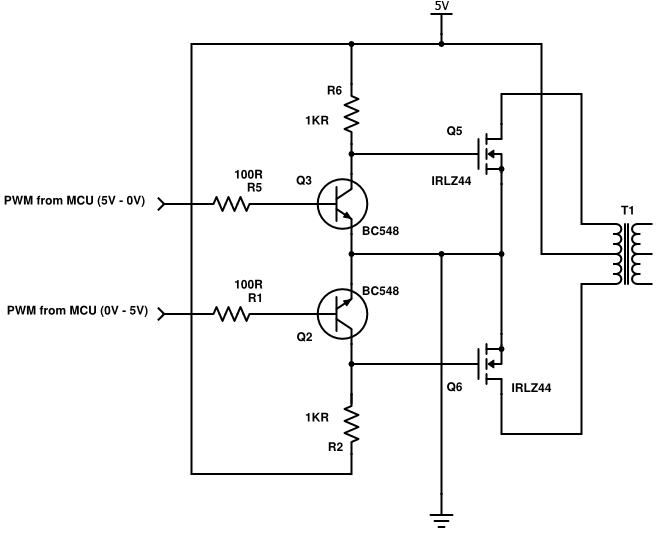
🔍 The Problem :
MOSFETs are widely used in power electronics, but switching them too fast can cause ringing, EMI, or even damage due to voltage spikes. Conversely, switching them too slowly increases heat loss and reduces efficiency. So how do you find the right balance?
🛠 The Solution :
To control switching speed, use a gate resistor between the driver and MOSFET gate. This resistor controls the rate at which the gate capacitor charges and discharges, directly influencing the rise and fall times.
💡 Practical Example :
Let’s say you’re designing a DC motor driver using an IRFZ44N MOSFET. Without a gate resistor, your scope shows high-frequency ringing and the MOSFET overheats. Adding a 10Ω gate resistor smooths the waveform and reduces EMI.
🔢 Sample Calculation :
Assume your gate charge is 25nC and you want a rise time of 100ns:
Gate current I=Q/t=25nC/100ns=0.25A
With a 5V gate drive, use Ohm’s Law:
R=V/I=5V/0.25A=20Ω (use 10–22Ω range based on testing)
🛒 Product Suggestion :
Looking for MOSFETs or flux for clean, reliable builds?
Shop now at SmartXProKits.in
🇮🇳 Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















