Understanding MOSFET Thermal Impedance: A Beginner’s Guide
The Problem :
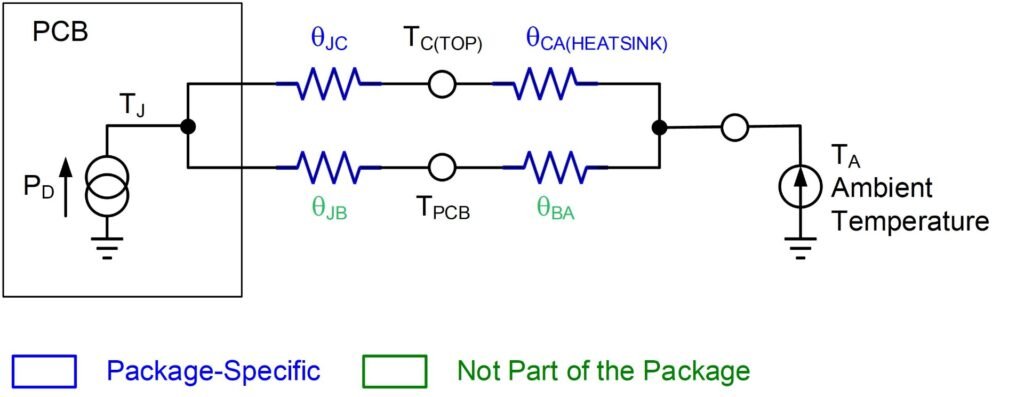
When using MOSFETs in circuits that handle high power, heat dissipation becomes a critical concern. Thermal impedance determines how efficiently heat moves from the MOSFET’s junction (internal core) to the surrounding environment. If the thermal impedance is too high, the heat stays trapped, leading to overheating, reduced efficiency, and possible damage.
The Solution :
To prevent overheating, you can reduce thermal impedance by:
✅ Using a heat sink to disperse heat.
✅ Applying thermal paste for better heat transfer.
✅ Ensuring proper PCB layout with adequate copper traces.
Practical Example :
Consider using an IRF540N MOSFET to drive a 12V LED strip drawing 5A. Without a heat sink, the MOSFET dissipates heat, raising the junction temperature significantly.
Sample Calculation :
If the MOSFET drops 1V across its drain-source terminals at 5A, the power dissipated is:
Power Loss=V×I=1V×5A=5W
With a thermal impedance of 3°C/W (junction-to-ambient), the temperature rise is:
Temp Rise=5W×3°C/W=15°C
Adding a heat sink with 1°C/W reduces the thermal impedance to 1°C/W, lowering the temperature rise to:
New Temp Rise=5W×1°C/W=5°C
Product Suggestions :
To ensure your MOSFET runs cooler and lasts longer, use:
🔹 IRF540N MOSFET – Ideal for high-power circuits.
🔹 Heat Sink for MOSFET – Lowers thermal impedance effectively.
Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















