SMPS Voltage Ripple Minimization: A Beginner’s Guide for Electronics Enthusiasts
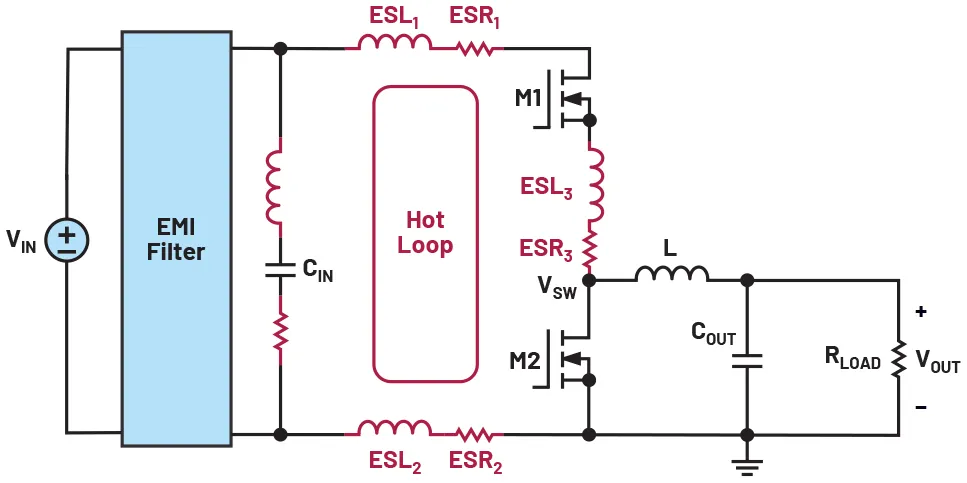
When building power supply circuits, one common issue you might encounter is voltage ripple in SMPS (Switch Mode Power Supply) designs. This ripple is essentially unwanted fluctuations in the output voltage, which can cause devices to malfunction or behave unpredictably. If you’ve noticed flickering lights or unstable performance in your projects, it’s likely due to ripple noise.
The Problem :
Voltage ripple occurs when the output voltage of an SMPS fluctuates, typically due to insufficient filtering or poorly sized components. In simple terms, think of it like water waves in a pond caused by dropping stones – the waves represent the ripple in your circuit.
The Solution :
To minimize ripple, we often add a capacitor across the output to filter out the fluctuations. By choosing the right capacitor size and type, you can smooth the output voltage and eliminate those unwanted waves. For beginners, it’s a good idea to start with electrolytic capacitors with a higher capacitance value.
Practical Example :
Imagine you’re powering a microcontroller from a 12V SMPS, and it’s acting erratically due to ripple. Adding a 470µF electrolytic capacitor at the output can smooth the voltage and stabilize your microcontroller’s performance.
Sample Calculation :
To size the capacitor, use the formula:
Ripple Voltage (V) ≈ (I * t) / C
Where:
- I is the load current,
- t is the ripple period,
- C is the capacitance value.
If you’re running a 100mA load and targeting a ripple voltage of 0.1V, and the period is 1ms, you would need a capacitor around 470µF.
Product Suggestion :
To effectively address voltage ripple, check out these components:
- Low ESR Capacitors (for better ripple suppression)
- MOSFETs (for efficient power switching)
Find high-quality, Made in India components at SmartXProKits and SmartXProKits.
Shop now at SmartXProKits.in and support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















