MOSFET Reverse Bias Protection: A Simple Guide for Electronics Enthusiasts
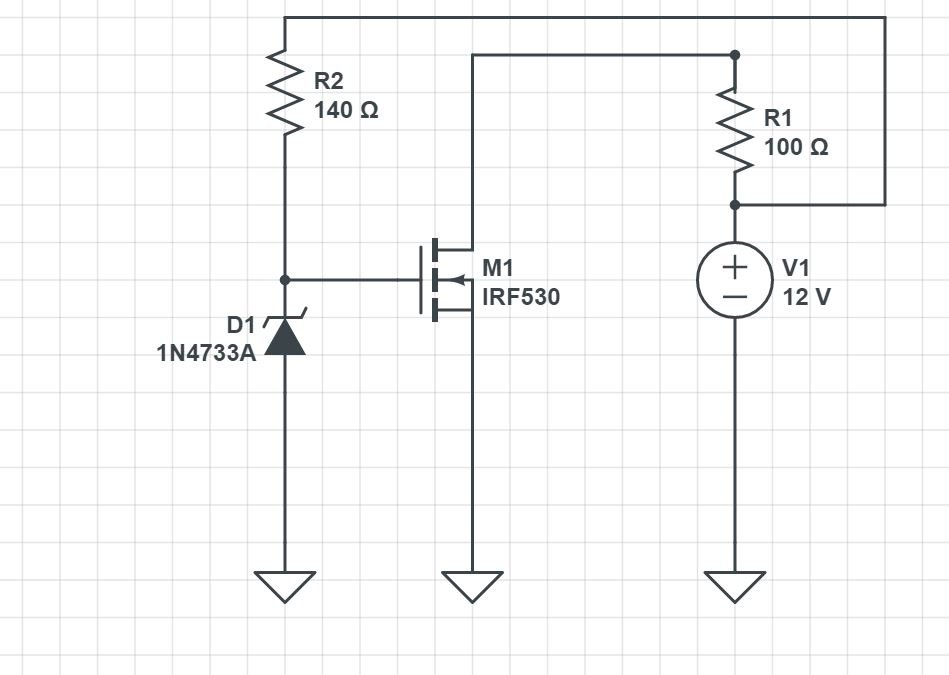
When working with MOSFETs in your electronics projects, one common issue that can occur is reverse biasing. Reverse bias happens when the voltage applied to the MOSFET’s gate or drain is in the wrong direction, potentially damaging the component. Understanding how to prevent this issue is crucial to ensuring the longevity of your circuits.
The Problem :
Reverse biasing occurs when a MOSFET’s gate or drain is connected to a voltage that opposes the normal operation of the device. In simple terms, applying voltage in the wrong direction can cause the MOSFET to malfunction or even break. This can happen easily in complex circuits or during prototyping, especially when switching power supplies or accidentally miswiring components.
The Solution :
To protect your MOSFET, you can add a diode or a clamping circuit in parallel with the MOSFET to block any reverse voltage. A Schottky diode, for example, has a low forward voltage drop and is ideal for protecting the MOSFET from reverse voltage spikes.
Practical Example :
Imagine you’re building a power switching circuit for a motor. If the power supply is connected with the wrong polarity, the MOSFET will face reverse bias. By adding a diode between the gate and ground, any reverse voltage will be safely diverted through the diode instead of damaging the MOSFET.
Sample Calculation :
Assuming a MOSFET with a gate threshold voltage (Vgs(th)) of 2V, and a Schottky diode with a forward voltage of 0.3V, the diode will conduct any voltage over 0.3V, protecting the MOSFET from damage. Always ensure the diode’s reverse voltage rating is higher than the expected operating voltage.
Related Products :
To ensure smooth prototyping, you can find high-quality MOSFETs and Schottky diodes Made in India. Explore our MOSFETs and diodes here!
Shop now at SmartXProKits.in.
Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















