MOSFET Over-Temperature Shutdown Circuits – Understanding and Solving the Issue
The Problem:
When working with MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors), heat is a common issue that can cause the device to shut down if it gets too hot. This is a protective feature called over-temperature shutdown. If the MOSFET gets too hot, it can fail, damaging your circuit and components. The main reason for overheating is excess current or inadequate heat dissipation.
The Solution:
To prevent MOSFETs from shutting down due to heat, you need to manage their temperature effectively. You can do this by ensuring proper heat sinking and using thermal shutdown circuits. A simple way to implement this is by adding a temperature sensor to monitor the MOSFET’s temperature. If it exceeds a threshold, the circuit can automatically reduce the power or shut down, keeping everything safe.
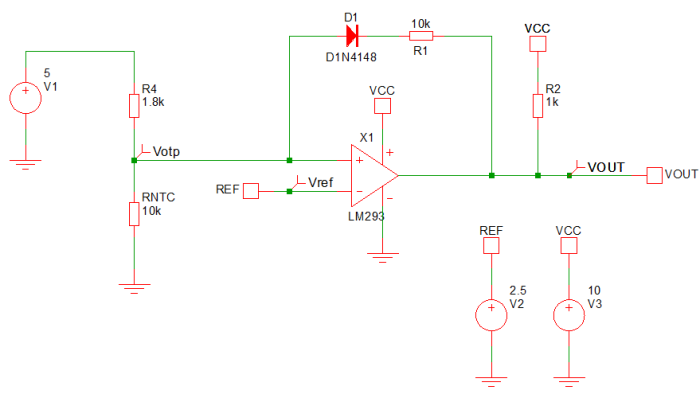
Practical Example:
Let’s say you’re building a motor controller circuit using a MOSFET, and it shuts down unexpectedly. The problem could be that the MOSFET is overheating due to excessive load. By adding a temperature sensor (like a thermistor) to the circuit, you can monitor the MOSFET’s temperature. If it reaches a certain level, you can have the circuit reduce the current flow or turn off the MOSFET, ensuring that it doesn’t overheat and cause damage.
Sample Calculation:
If your thermistor has a resistance of 10kΩ at room temperature and changes by 2kΩ per °C increase, you can calculate the voltage drop across the thermistor at a certain temperature.
For example, at 50°C, the resistance would be 20kΩ, and if paired with a 10kΩ resistor, you can calculate the voltage divider output.
This helps determine when the MOSFET needs to shut down.
Products Suggestion:
For your projects, consider using MOSFETs and thermal sensors. Both can be found easily at SmartXProKits. Shop now at SmartXProKits.
Support our work and India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















