Low Power IoT Device Power Supply Design: A Beginner’s Guide
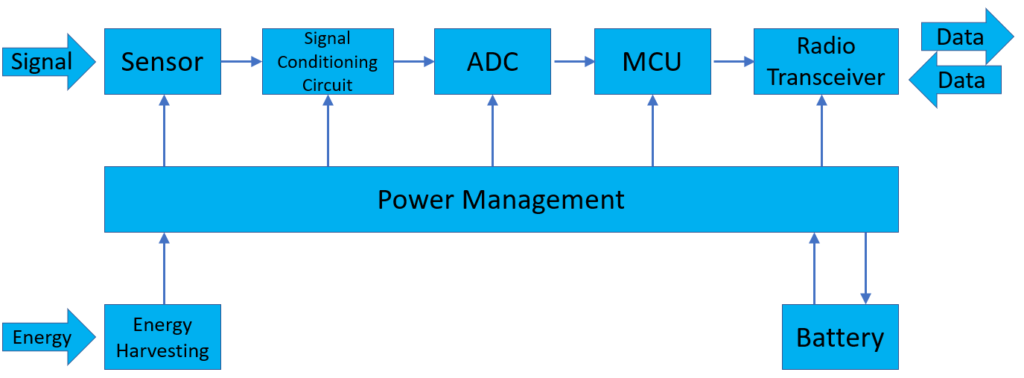
As IoT (Internet of Things) devices become more common in everyday life, ensuring efficient power management is key, especially for low-power devices. But what happens when your IoT device doesn’t run efficiently and drains more power than expected? This is a common issue in power supply design. Here’s how to fix it, in simple terms.
The Problem :
IoT devices often run on battery power. Without proper power supply design, they can drain batteries too quickly, leading to short device lifespans and increased maintenance. The key is to use low-power components and efficient power conversion techniques, ensuring devices consume as little energy as possible.
Practical Example :
Imagine you’re designing a smart home temperature sensor. If the sensor isn’t optimized for low power, the battery might only last a few weeks. However, by adding a low-dropout regulator (LDO) and using energy-efficient sensors, you can extend the battery life for months.
Sample Calculation :
For a typical low-power IoT sensor, let’s say it consumes 5mA at 3.3V.
The battery provides 3.7V.
The current required from the LDO can be calculated as:
Power (P) = Voltage (V) x Current (I) P = 3.3V * 0.005A = 0.0165W (16.5mW)
The LDO should have an efficiency of around 90%, making it a perfect choice for battery-powered devices.
Recommended Products :
Looking for quality, energy-efficient components? Check out Low Dropout Regulators and Low-Power Sensors for your next project. Shop now at SmartXProKits.in and support India’s innovation with Made in India components!




















