3D Printed Robotic Hand For DIY Projects(Electronic Components Not Included) - 056
Top mount 16x2 LCD Display Holder for DIY Projects - 049
24-Pin Panel Mounted Male-Female Connector HE-24 Industrial Heavy Duty (300V 5A)
16x2 LCD Display Holder For DIY Project - 059
Enclosure Box For D1 Mini,Gas Sensor,DHT11 Sensor (Components not included)
16x2 display holder with rotrary encoder support - 047
Gas Sensor Panel Mounted Enclosure For Automation (Sensor not included)
E18-D80NK NPN-NO Adjustable IR Proximity Sensor Switch – 3-80cm Range for Obstacle Detection
Adjustable Sensor Holder For Industrial Automation
3-in-1 Aluminum Heat Sink Set for Raspberry Pi 3/4 – Efficient Cooling for Overclocking and High Power Use
AR28 Nano I/O Expansion Shield for Arduino | Sensor & Servo Breakout Board
4x3 Keypad Panel Mounted Enclosure For DIY Project (Keypad not included)
DIY Robotic Hand Combo Kit – Arduino-Based Smart Hand Project | Wireless Control | STEM Learning Kit
230V AC to 48V DC Converter, 1A – Rail Mount Power Supply for Industrial and Automation Applications
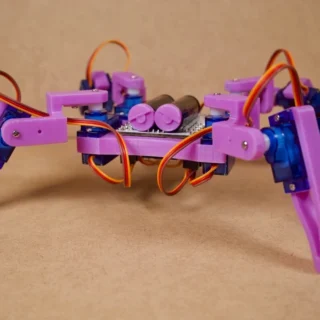
Quadruped Spider Robot Combo Kit – -4 Legged DIY STEM Crawling Robot with Servo Motors
16x2 LCD Display with Arduino Nano Board Enclosure for DIY Projects
28BYJ-48 Stepper Motor Holder For DIY Projects + With Stepper Motor and Driver
DHT11 Sensor module panel mount holder for Automation -048
28BYJ-48 Stepper Motor Holder For DIY Projects (Without Stepper Motor)
LM2596/Xl6009 Holder for DIY Projects -050
3D Printed Robotic Hand For DIY Projects(Electronic Components Not Included) - 056
Top mount 16x2 LCD Display Holder for DIY Projects - 049
24-Pin Panel Mounted Male-Female Connector HE-24 Industrial Heavy Duty (300V 5A)
16x2 LCD Display Holder For DIY Project - 059
Enclosure Box For D1 Mini,Gas Sensor,DHT11 Sensor (Components not included)
16x2 display holder with rotrary encoder support - 047
Gas Sensor Panel Mounted Enclosure For Automation (Sensor not included)
E18-D80NK NPN-NO Adjustable IR Proximity Sensor Switch – 3-80cm Range for Obstacle Detection
Adjustable Sensor Holder For Industrial Automation
3-in-1 Aluminum Heat Sink Set for Raspberry Pi 3/4 – Efficient Cooling for Overclocking and High Power Use
AR28 Nano I/O Expansion Shield for Arduino | Sensor & Servo Breakout Board
4x3 Keypad Panel Mounted Enclosure For DIY Project (Keypad not included)
DIY Robotic Hand Combo Kit – Arduino-Based Smart Hand Project | Wireless Control | STEM Learning Kit
230V AC to 48V DC Converter, 1A – Rail Mount Power Supply for Industrial and Automation Applications
Quadruped Spider Robot Combo Kit – -4 Legged DIY STEM Crawling Robot with Servo Motors
16x2 LCD Display with Arduino Nano Board Enclosure for DIY Projects
28BYJ-48 Stepper Motor Holder For DIY Projects + With Stepper Motor and Driver
DHT11 Sensor module panel mount holder for Automation -048
28BYJ-48 Stepper Motor Holder For DIY Projects (Without Stepper Motor)
LM2596/Xl6009 Holder for DIY Projects -050
Science Project Models
Rated 4.57 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Alcohol detection alarm DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.47 out of 5 based on 19 customer ratings
LDR Based Light Detection DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT Ready (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.14 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Design of Alcohol Detection System for Car DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.36 out of 5 based on 14 customer ratings
Heat Sensor Using NTC DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Wheelchair Fall Detection DIY Experiments Science STEM KIT Science Project Model (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.57 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Laser Secutiry system for Bank DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.25 out of 5 based on 8 customer ratings
Automatic Temperature Control Fan DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled) – 100% Tested
Rated 4.71 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Alcohol Detection for Vehicles DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM Kit (Assembled, 100% Tested)
Rated 4.00 out of 5 based on 1 customer rating
LDR based Sunset Lamp control Ready DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Anti Blast Landmine Project for Indian Army | Inspire Award Project Kit | Science Model | STEM Kit (Assembled, 100% Tested)
Rated 4.86 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Rain Water Alarm Sensor DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.57 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Rain Alarm Project DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled, 100% Tested)
Rated 4.00 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Smoke Detection for Industrial safety DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.46 out of 5 based on 26 customer ratings
Automatic Pump ON/OFF Base on Fire DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 1 customer rating
LDR Based darkness Detection DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT Ready (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.48 out of 5 based on 23 customer ratings
Switch circuit of pole light using LDR DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT Ready (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.68 out of 5 based on 19 customer ratings
Theft Alarm Using IR Sensor DIY Experimentsl Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Third Eye for Blind – Proximity Sensor Eye Glasses DIY Experiments STEM KIT Science Project Model (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.41 out of 5 based on 34 customer ratings
Automatic Irrigation System DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.53 out of 5 based on 19 customer ratings
Touch Switch DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.57 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Alcohol detection alarm DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.47 out of 5 based on 19 customer ratings
LDR Based Light Detection DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT Ready (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.14 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Design of Alcohol Detection System for Car DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.36 out of 5 based on 14 customer ratings
Heat Sensor Using NTC DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Wheelchair Fall Detection DIY Experiments Science STEM KIT Science Project Model (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.57 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Laser Secutiry system for Bank DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.25 out of 5 based on 8 customer ratings
Automatic Temperature Control Fan DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled) – 100% Tested
Rated 4.71 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Alcohol Detection for Vehicles DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM Kit (Assembled, 100% Tested)
Rated 4.00 out of 5 based on 1 customer rating
LDR based Sunset Lamp control Ready DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Anti Blast Landmine Project for Indian Army | Inspire Award Project Kit | Science Model | STEM Kit (Assembled, 100% Tested)
Rated 4.86 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Rain Water Alarm Sensor DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.57 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Rain Alarm Project DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled, 100% Tested)
Rated 4.00 out of 5 based on 7 customer ratings
Smoke Detection for Industrial safety DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.46 out of 5 based on 26 customer ratings
Automatic Pump ON/OFF Base on Fire DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 1 customer rating
LDR Based darkness Detection DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT Ready (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.48 out of 5 based on 23 customer ratings
Switch circuit of pole light using LDR DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT Ready (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.68 out of 5 based on 19 customer ratings
Theft Alarm Using IR Sensor DIY Experimentsl Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Third Eye for Blind – Proximity Sensor Eye Glasses DIY Experiments STEM KIT Science Project Model (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.41 out of 5 based on 34 customer ratings
Automatic Irrigation System DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Rated 4.53 out of 5 based on 19 customer ratings
Touch Switch DIY Experiments Science Project Model STEM KIT (Assembled), 100% Tested
Most Rated Products
Cute Unicorn DIY Coloring Set 3D Printed | 3 Mini Horse Keychains for Kids | Paintable Fantasy Toys for Girls, Return Gifts & Creative Craft Activities
₹499.00 Original price was: ₹499.00.₹399.00Current price is: ₹399.00. + GST
Wall Mount Charger Holder for Bajaj Chetak EV – Cable Organizer Stand for Home Charging – Compact, Durable Wall Dock
₹1,200.00 Original price was: ₹1,200.00.₹999.00Current price is: ₹999.00. + GST
Pocket Creature DIY Coloring Set 3D Printed | 4 Mini Keychain Toys for Kids | Paintable Cute Character Models for Return Gifts, School & Art Fun
₹499.00 Original price was: ₹499.00.₹399.00Current price is: ₹399.00. + GST
Low-Cost Walking Robot "Grillo" | Complete Working STEM Project for School – Simple Design with Long Legs & Motor-Driven Movement
₹799.00 Original price was: ₹799.00.₹499.00Current price is: ₹499.00. + GST
Love Labu Keychain 3D Printed | DIY Coloring Keyring Toy for Kids & Gifting | Cute Cartoon-Style Mini Figurine for Bags, Bikes, School & Return Gifts
₹399.00 Original price was: ₹399.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. + GST
Walking Robot School Project | Fully Working STEM Model for Students – 3D Printed Biped Robot with Motors & Battery – Ideal for Science Exhibitions
₹799.00 Original price was: ₹799.00.₹499.00Current price is: ₹499.00. + GST
Karate Labu Keychain 3D Printed | DIY Coloring Key Ring for Kids & Collectors | Cartoon Style Mini Figurine Keychain for Bags, Bikes & Gifts
₹599.00 Original price was: ₹599.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. + GST
Arduped Biped Robot Frame | Walking Robot Body Kit 3D Part – DIY STEM Robotics Project (Electronics Not Included)
₹799.00 Original price was: ₹799.00.₹399.00Current price is: ₹399.00. + GST
Under Monitor Pen & Sticky Note Holder 3D Printed | Space-Saving Desk Organizer | Minimalist Office Accessory for Pens, Notes & Stationery
₹1,200.00 Original price was: ₹1,200.00.₹899.00Current price is: ₹899.00. + GST
3D Printed Micro Robot Arm Frame | DIY Mini Robotic Arm Body Kit only , Elecrtonics not included– Ideal for STEM & Robotics Projects
₹799.00 Original price was: ₹799.00.₹499.00Current price is: ₹499.00. + GST
Knight of the Quill – 3D Printed Medieval Knight Pen Holder | Unique Desk Organizer | Cool Gift for Office, Students, Gamers & History Lovers
₹1,200.00 Original price was: ₹1,200.00.₹699.00Current price is: ₹699.00. + GST
Rope Climbing Robot School Project | Ready-to-Use STEM Educational Model with Motor & Pulley System – Ideal for Science Exhibitions
₹799.00 Original price was: ₹799.00.₹499.00Current price is: ₹499.00. + GST
Stylish Modern Bicycle Bottle Holder | Lightweight & Durable Water Bottle Cage | Elegant 3D Printed Cycle Accessory for MTB, Road & Hybrid Bikes
₹1,200.00 Original price was: ₹1,200.00.₹699.00Current price is: ₹699.00. + GST
3D Printed Quadruped Robot Frame | Q1 Lite Body Kit for 4-Leg Walking Robot – 3D Parts Only
₹799.00 Original price was: ₹799.00.₹499.00Current price is: ₹499.00. + GST
Warrior Pen Holder 3D Printed | Unique Desk Organizer for Office & Home | Cool Stationery Holder for Kids, Students & Gamers | Table Decor Figurine
₹1,200.00 Original price was: ₹1,200.00.₹799.00Current price is: ₹799.00. + GST
3D Printed Micro 105 FPV Quadcopter Frame | Lightweight Body Shell for 8.5mm Motors & Micro Flight Boards – DIY Drone build (Frame Only Electronic Not Included)
₹299.00 Original price was: ₹299.00.₹199.00Current price is: ₹199.00. + GST
Chubby Pink T-Rex Dino Pencil Holder – Fun & Functional Desk Organizer | Best Gift for Your Chubby Friend (Copy)
₹899.00 Original price was: ₹899.00.₹499.00Current price is: ₹499.00. + GST
Hyperboloid Pen Holder | Modern Desk Organizer for Pens, Brushes, and Stationery – Artistic Spiral Design
₹599.00 Original price was: ₹599.00.₹499.00Current price is: ₹499.00. + GST
Wall Mount Charger Holder for TVS iQube EV – Cable Organizer for Home Charging – Wall Dock for iQube Electric Scooter Charger
₹1,200.00 Original price was: ₹1,200.00.₹799.00Current price is: ₹799.00. + GST
3D Printed Snorlax Apple Watch Stand | Cute Cartoon-Themed Charging Dock for Apple Watch Series – Desk Organizer & Nightstand Accessory
₹599.00 Original price was: ₹599.00.₹399.00Current price is: ₹399.00. + GST
BIG SAVING
Single Delivery charges for Multiple Items
AWESOME SUPPORT
Our support lines are open from 10am to 6pm, to support all your queries.
FAST DELIVERY
Fast delivery and Free Shipment on all order above 900 Rs .
SECURE CHECKOUT
We follow highest security standards to make your transaction safe


 Industrial Automation
Industrial Automation 3D Printing
3D Printing Electronic
Electronic Hardware
Hardware RC Plane and Drone
RC Plane and Drone Robotic
Robotic Science Fair Project
Science Fair Project