Mastering MOSFET Switching Frequency for Better Efficiency
The Problem :
Choosing the wrong switching frequency in a MOSFET circuit can cause excessive heat and power loss. High frequencies increase switching losses, while low frequencies make the circuit inefficient.
The Solution :
To select the right switching frequency:
Identify Load Requirements: Check voltage and current demands.
Evaluate MOSFET Specs: Focus on gate charge (Qg) and drain-source capacitance (Cds).
Optimal Range: For most circuits, a range between 20 kHz to 200 kHz offers the best balance between efficiency and heat management.
Practical Example :
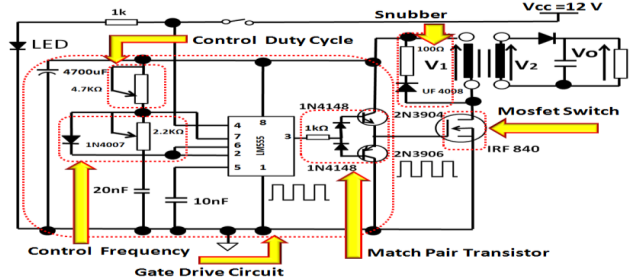
If you’re driving a 12V DC motor using a MOSFET IRFZ44N, operating it at 50 kHz maintains efficient operation without overheating. But if the frequency increases to 200 kHz, the MOSFET may generate excess heat, requiring a heatsink.
Sample Calculation :
For a MOSFET with Qg = 63 nC and gate driver current of 500 mA:
Switching Time (t) = IQg = 0.563×10−9≈126ns
At 100 kHz, the MOSFET switches efficiently with minimal power loss.
Recommended Products :
Ensure smooth switching with quality MOSFETs and gate driver ICs:
Shop now at SmartXProKits.in and support India’s innovation—buy from our Make in India site!




















